Getting Started with Comodo RSA Certification Authority
Comodo (now Sectigo) RSA Certification Authority is one of the most well-established and trusted root certificate authorities that form the backbone of website authentication and encrypted communication on the Internet. It is operated by Comodo CA Limited, which has been a leading provider of TLS/SSL certificates since 1998.
The company has its roots in security software and services. Comodo offers a wide range of certificate products to meet needs, including SSL/TLS server certificates for domains, code signing certificates, secure email certificates, and more.
Comodo RSA root certificates are embedded in all major operating systems, browsers, and mobile devices. This allows Comodo to seamlessly enable trusted TLS connections between servers and clients across the Internet. Through its SSL/TLS certificates, Comodo currently secures over 100 million internet sites globally.
Key Takeaways
- COMODO RSA Certification Authority is one of the most well-known and trusted root certificate authorities, anchoring the chain of trust for SSL/TLS certificates.
- Root certificates like Comodo RSA form the backbone of web security by enabling encrypted TLS connections between browsers and servers.
- Comodo RSA root certificates come pre-installed on all major operating systems, browsers, and mobile devices.
- The certificate chain links end-entity certificates used by websites to the trusted root CA through intermediate certificates.
- Intermediate CAs like Comodo RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA bridge the gap between the root and domain certificates.
- Comodo RSA uses industry-standard 2048-bit RSA encryption and provides extensive certificate lifecycle management.
- Comodo RSA certificates instill user trust, enable compliance, and provide SEO value for secured sites.
Importance of a Trusted Root Certificate Authority
Root certificate authorities occupy the top position in the public key infrastructure (PKI) hierarchy, which secures communications over networks. They are designated as ‘trust anchors,’ meaning their certificates do not need any further verification.
Browsers and operating systems come bundled with automatically trusted root CA certificates from authorities like Comodo RSA. Relying parties can verify certificates issued by intermediate CAs and domains through their trusted root certificates.
This eliminates the need for manually distributing and installing root certificates on each device. Comodo RSA root certificates, hence, provide the foundation on which Comodo certificates are inherently trusted.
What is a Root Certificate
A root certificate is a digital certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority to identify itself and enable the establishment of a chain of trust. It contains details like:
- Public key to verify its digital signature
- Identity of root CA
- The validity period of the certificate
- Purpose declaration of being a trust anchor
Root certificates are self-signed, meaning their digital signature is verified using their public key. They form an integral base for confirming the validity of all certificates issued by the CA.
Role f Root Certificates in The Chain of Trust
Root CAs issue intermediate certificates that inherit their trust status. These intermediate CAs, in turn, issue end-entity certificates to websites and other parties.
Relying parties can verify an end-entity certificate by checking the issuer’s certificate and repeating this until the root CA certificate is reached. This ability to validate certificates along the chain makes root certificates critical.
Pre-Installation of Root Certificates In Browsers And Devices
For the PKI hierarchy to work, root certificates need to be distributed to user devices and software. Top browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc, and operating systems like Windows, iOS, and Android come bundled with root certificates from trusted CAs like Comodo.
This allows the root CA certificates to be automatically trusted without requiring users to install them manually. Device OEMs and software vendors determine which root CAs to embed based on criteria like longevity, reputation, standards compliance, and security.
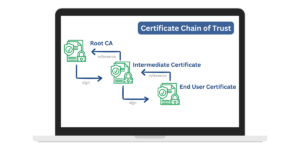
What is a Certificate Chain?
A certificate chain is a sequence of certificates connecting a leaf certificate to the root CA certificate. It enables relying parties to validate the leaf certificate’s authenticity.
For instance, the certificate chain for a domain-validated certificate would look like this:
Root CA certificate -> Intermediate CA certificate -> Domain certificate
The chain establishes a chain of trust from root to domain.
How Certificates are Linked from Root to End-User
The certificates in a chain are linked through the issuer and subject fields. The subject of each certificate is the entity it identifies. The issuer identifies the CA that issued the certificate.
In a 3-certificate chain:
- Root CA certificate:
- Subject: Root CA
- Issuer: Root CA (self-signed)
- Intermediate CA certificate
- Subject: Intermediate CA
- Issuer: Root CA
- Subject: example.com
- Issuer: Intermediate CA
- Subject: example.com
- Issuer: Intermediate CA
This illustrates the upward link from domain to root CA. The root CA is trusted, which makes the entire chain valid.
Importance of The Complete Certificate Chain For Security
To trust a certificate, relying parties must receive the complete certificate chain, not just the domain certificate. The intermediate certificates are required to bridge the gap between domain and root certificate.
If the intermediate certs are missing, the domain certificate cannot be successfully validated. This will trigger browser errors about untrusted connections.
What are the Purpose of Intermediate Certificates
Intermediate certificates are used to establish a chain of trust between the trusted root CA and end-entity certificates issued to domains.
Some key benefits of using intermediate certificates are:
- Limits exposure of root CA: The root private key can be offline while intermediate CAs issue certificates.
- Administrative delegation: Intermediates can be bound by different policies.
- Lifecycle management: Intermediates can be renewed independently of root CA.
- Troubleshooting: Issues can be isolated to intermediates.
How Intermediate Certs Connect the Root to End-User Certs
The root CA issues the intermediate CA’s certificate, and the root’s signature is required to validate it. When the intermediate CA issues end-entity certificates, these contain the intermediate’s signature.
By linking the intermediates to the trusted root, a chain of validity is created. The root’s self-signed certificate is at the top, intermediates in the middle, and end-entities at the bottom.
Reasons For Using Intermediate Certificates
Intermediates provide flexibility to the PKI and make certificate management easier. Some key advantages are:
- Limit exposure of root CA: Keeping the root offline minimizes exposure.
- Partition control: Different intermediates can have different policies.
- Revoke intermediates independently: Root CA need not be affected.
- Lifespan limitation: Intermediates can be short-lived while the root is long-term.
- Troubleshoot issues: Issues can be traced to specific intermediates.
- Flexible cross-signing: Intermediates can chain to multiple roots.
Why Comodo RSA Certification Authority is Trusted
Comodo RSA Certification Authority has established a reputation as being one of the most trusted root CAs. Key facts supporting its status as a leading certificate authority include:
- Founded in 1998, Comodo is a CA pioneer with over 20 years of experience.
- Comodo RSA root certificates are embedded in all major OS and browsers.
- It has issued over 200 million certificates to date.
- Comodo handles domain validation at scale, issuing high volumes of SSL/TLS certificates.
- It has a robust infrastructure spanning top data center locations.
- Comodo conforms to rigorous industry standards like WebTrust and CAB audits.
Technical Details of Comodo’s RSA-Based Encryption
Comodo RSA certificates utilize industry-standard RSA public-key encryption with a 2048-bit key length.
Some details include:
- It uses secure algorithms – SHA256 for hashing and RSA with 2048-bit keys.
- Comodo rotates root certificates periodically, and it is currently on the AddTrust External CA Root.
- It complies with CA/B Forum Baseline Requirements for managing SSL/TLS certificates.
- Comodo operates within a secure hardware-based PKI infrastructure.
- It maintains redundancy across data centers and has robust disaster recovery abilities.
Certificate Management Features Offered by Comodo
Comodo provides extensive capabilities for managing the SSL/TLS certificate lifecycle. This enables customers to meet security best practices.
Features include:
- Certificate issuance, renewal, and reissuing processes are automated.
- It supports features like OCSP stapling and CDN certificate distribution.
- Certificate revocation is enabled through CRL and OCSP.
- Comodo provides certificate transparency logging across roots.
- There are mechanisms to detect and act on misissued certificates.
- Browsers are updated about distrusting certificates in incidents.
What are the Benefits of Using Comodo RSA Certificates
Improved Website Security and User Trust
Using an SSL/TLS certificate issued by Comodo RSA Certification Authority provides top-notch security for websites and applications, improving user trust.
Some key benefits are:
- Users can validate site identity via the green padlock and Comodo brand.
- The 2048-bit RSA encryption protects data in transit from man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Strict domain validation prevents spoofing and phishing attempts.
- Revocation capability quickly turns off compromised certificates.
- Up-to-date international browsers and devices recognize Comodo RSA.
- It is backed by a $250,000 warranty that covers reliance losses.
With Comodo RSA certificates safeguarding the TLS handshake and data transfer, users can trust sites to be secure.
Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Comodo conforms to all major industry standards governing the issuance and management of SSL/TLS certificates. This helps websites using Comodo certificates meet compliance needs.
- Comodo follows requirements in the CA/B Forum Baseline Requirements and EV Guidelines.
- Its certificates adhere to browser root programs for wider acceptance.
- Comodo enforces procedures that are aligned with WebTrust Principles and Criteria.
- It meets EU eIDAS regulation standards for electronic trust services.
- The certificates can comply with organizational policies and external regulations.
- Comodo undergoes regular external assessments and audits.
Enhanced Search Engine Visibility and Rankings
Websites protected using Comodo RSA SSL certificates benefit from improved search engine visibility. Key aspects include:
- Enables HTTPS version of sites to be indexed over HTTP counterparts.
- Google and Bing use HTTPS as a positive signal in ranking algorithms.
- Increases user trust and time spent due to added security.
- Prevents security warnings that cause visitors to leave.
- Comodo is universally recognized for consistent site branding.
- Performs stringent domain validation vetting for all certificates.
Final Thoughts
Implementing encryption is vital for internet security. While domains use certificates from various CAs, these are all anchored by pre-trusted root authorities. Comodo RSA Certification Authority is one of the most reliable and recognizable roots that secure connections.
By choosing Comodo RSA-issued certificates for their infrastructure, organizations, and users can benefit from robust encryption and industry-leading certificate lifecycle management. This helps create a seamless TLS environment where visitors can access sites safely using trusted SSL certificates.
FAQs Related to COMODO RSA Certification Authority
What is the Comodo RSA Certification Authority?
The Comodo RSA Certification Authority (CA) is one of the most trusted root certificate authorities that are pre-installed on major browsers and devices. It issues end-entity TLS/SSL certificates through intermediate CAs that chain up to the Comodo RSA root CA certificate. This allows relying parties to validate the chain of trust for secure connections.
Why is Comodo RSA CA trusted?
Comodo RSA root certificates are inherently trusted because they are embedded in platforms like Microsoft, Apple, Mozilla, Android, and billions of devices. Comodo has maintained its reputation as a leading CA for over 20 years and follows industry best practices around issuing and managing digital certificates.
What encryption does Comodo RSA use?
Comodo RSA certificates utilize 2048-bit RSA encryption with SHA-256 for hashing. This provides secure encryption strength that cannot be compromised by brute force. Comodo regularly updates its infrastructure to maintain optimal algorithms and key lengths.
What certificates can I get from Comodo RSA?
Through its intermediate CAs, Comodo RSA provides a wide range of certificate products. Main options include DV SSL, OV SSL, and EV SSL certificates for websites, multi-domain SAN certificates, code-signing certificates, client certificates for email signing, and more.
How does Comodo RSA manage certificate lifecycles?
Comodo RSA uses industry-leading procedures for issuance, renewal, revocation, and reissuance. It provides capabilities like automated issuance workflows, OCSP stapling support, CDN distribution of certificates, and CRL/OCSP-based revocation, enabling customers to maintain best practices for SSL/TLS certificate management.

Priya Mervana
 Verified Web Security Experts
Verified Web Security Experts
Priya Mervana is working at SSLInsights.com as a web security expert with over 10 years of experience writing about encryption, SSL certificates, and online privacy. She aims to make complex security topics easily understandable for everyday internet users.