Introduction
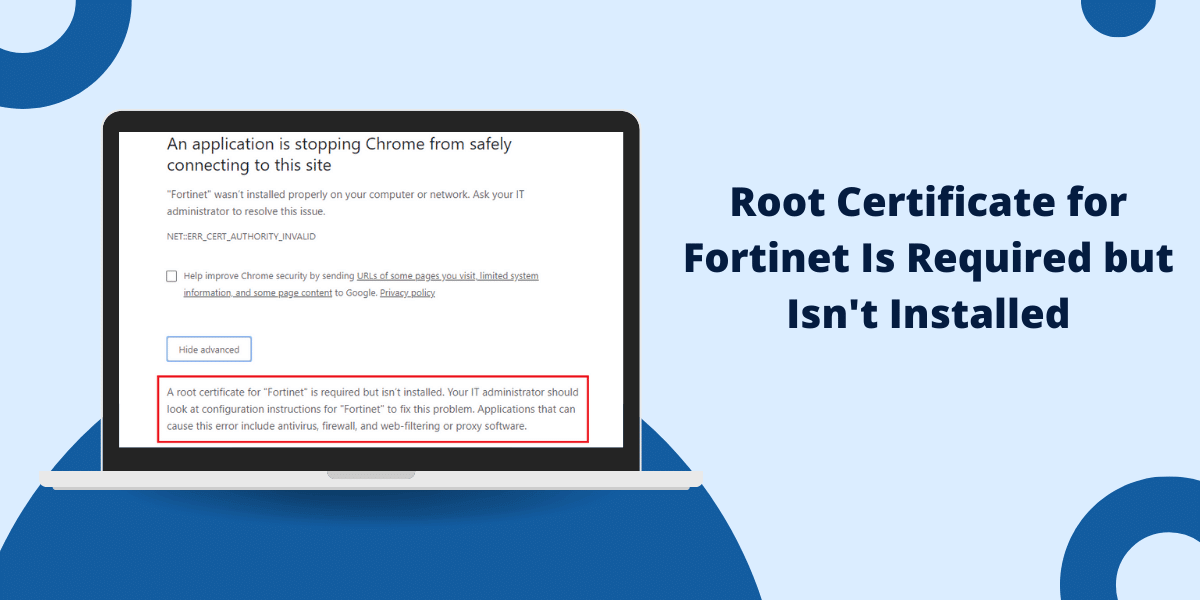
Fortinet firewalls like FortiGates utilize SSL inspection to decrypt encrypted HTTPS traffic for scanning and security purposes. To decrypt the traffic, Fortinet impersonates the recipient by presenting its own certificate to the client. The client’s device sees this unfamiliar Fortinet certificate and considers it invalid, which triggers certificate errors like “Fortinet root certificate required but not installed”.
To avoid such errors, the Fortinet root certificate must be installed on all client devices accessing inspected HTTPS websites through the Fortinet firewall. This establishes trust between the client and Fortinet, allowing seamless HTTPS inspection.
Equipped with this knowledge, you will be able to quickly troubleshoot and fix the “Fortinet root certificate required but not installed” error when it occurs on your network.
Overview of the “Fortinet Root Certificate Required but Not Installed” Error
Whenever you browse to an HTTPS website through a Fortinet firewall with SSL inspection enabled, the following sequence of events occurs:
- Your client sends an HTTPS request to access the secure website.
- The Fortinet firewall intercepts the request and impersonates the website using its own certificate.
- Your client receives the Fortinet firewall’s certificate instead of the actual website’s certificate.
- Your client checks if the Fortinet certificate is trusted.
- If the Fortinet root certificate is missing from your device, the certificate is considered invalid.
- An error is triggered – “Fortinet root certificate required but not installed”.
This error indicates that your client does not trust the Fortinet firewall’s certificate as the signing root certificate is missing.
To trust the Fortinet firewall’s certificate, you need to install the Fortinet root certificate on your device. This establishes trust and allows the Fortinet firewall to seamlessly inspect HTTPS traffic.
Troubleshooting Checklist for “Fortinet Root Certificate Required but Not Installed” Error
Follow this checklist to troubleshoot and fix the “Fortinet root certificate required but not installed” error:
- Verify SSL Inspection is Enabled on the Fortinet Firewall
- Confirm the Root Certificate Downloaded Matches Your Fortinet Firewall
- Check if the Root Certificate is Installed Correctly on Client Devices
- Verify There are No Interception or Inspection Issues
Step 1: Verify SSL Inspection is Enabled on the Fortinet Firewall
- Log into your Fortinet firewall and navigate to Policy & Objects > Security Profiles.
- Check if an SSL inspection profile like “certificate-inspection” is enabled here.
- If SSL inspection is disabled, encrypted HTTPS traffic will flow through without decryption and no Fortinet certificate will be presented to clients.
Step 2: Confirm the Root Certificate Downloaded Matches Your Fortinet Firewall
- Different firmware versions may use different root certificates. When downloading the root certificate, make sure it matches your Fortinet firewall’s firmware version.
- You can check your firewall’s firmware version under System > Dashboard.
Step 3: Check if the Root Certificate is Installed Correctly on Client Devices
- The methods to install the Fortinet root certificate vary across operating systems and browsers. Make sure the certificate is installed correctly for the specific client device and browser.
- For Windows, ensure the root certificate is installed under Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
- On Mac, the Fortinet root certificate should be installed in Keychain Access and marked as “Always Trust”.
- For Firefox browsers, manually import the certificate in Firefox’s certificate manager.
Step 4: Verify There are No Interception or Inspection Issues
- Use packet capturing tools like Wireshark to sniff network traffic between your client and the Fortinet firewall.
- Check if any intermediary devices like proxies or additional firewalls are intercepting traffic and replacing the Fortinet certificate with their own.
- This can also cause certificate errors.
These steps will help isolate and troubleshoot the “Fortinet root certificate required but not installed” error.
Downloading and installing the Fortinet Root Certificate
Once you have confirmed that SSL inspection is enabled and necessary prerequisites are met, you can download and install the Fortinet root certificate with these steps:
- Log into your Fortinet firewall and go to Security Profiles > SSL/SSH Inspection.
- Locate the certificate-inspection SSL inspection profile and click “Download Certificate”. This downloads the Fortinet root certificate file.
- Install the downloaded root certificate into the trusted certificate store based on your device’s operating system:
- Windows: Double click the certificate file and install it under Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
- Mac: Double click the certificate file to open Keychain Access. Select the certificate, expand Trust, and set to Always Trust.
- Linux: Copy the certificate file to /usr/local/share/ca-certificates and run ‘update-ca-certificates’.
- Chrome/Firefox browsers: Manually import the certificate in Chrome/Firefox certificate manager.
- Restart your browser or device for the changes to take effect.
- Try accessing the HTTPS websites again. The error should no longer appear.
Take note of the certificate expiry date and remember to renew the Fortinet root certificate when it expires to avoid issues.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips for Fortinet Certificate Errors
Here are some additional troubleshooting tips for Fortinet root certificate issues:
- Flush browser caches and restart the browser after installing the certificate. Cached certificate errors may persist otherwise.
- Try accessing the HTTPS websites using an incognito or private browser window. This uses a clean certificate store unaffected by caching.
- Temporarily disable SSL inspection on the Fortinet firewall for troubleshooting purposes. This allows access to the actual websites with no inspection.
- Verify if the error appears consistently across multiple client devices and operating systems. Intermittent issues may indicate a flaky network.
- Inspect HTTP response headers for error codes like ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID to isolate the exact certificate issue.
- Use online SSL testing tools to diagnose and confirm the specific certificate problem.
- Contact Fortinet support with packet captures, debug logs and troubleshooting details if the problem persists.
Preventing Certificate Warnings by Using Self-Signed Certificates
Fortinet firewalls use a default Fortinet certificate for SSL inspection that produces certificate warnings.
You can prevent warnings by using custom self-signed certificates instead. Here is an overview of the steps:
- Create a self-signed certificate– Use OpenSSL Commands to generate a new self-signed certificate and private key. Set a long validity period.
- Upload certificate to Fortinet firewall– In the GUI, go to System > Certificates and import the new certificate as a Local Certificate.
- Configure inspection profile– Edit your SSL inspection profile to use the new self-signed certificate for inspection instead of the default Fortinet certificate.
- Install certificate on clients– Download the new self-signed certificate from the Fortinet firewall and install it as a trusted root certificate on all clients.
This allows the Fortinet firewall to use your own trusted certificate for SSL inspection rather than the default cert that causes trust errors.
While more complex to implement, this approach prevents those errors altogether on your network.
Automating Fortinet Root Certificate Installation
For large networks, manually installing the Fortinet root certificate on each client device can be cumbersome.
You can automate bulk certificate installation using:
- MDM solutions – Use a mobile device management platform like Microsoft Intune to push and install the Fortinet root certificate onto managed devices.
- GPOs/Scripts – Leverage Active Directory group policies or scripts to distribute and install the Fortinet root certificate on domain-joined Windows devices.
- Certificate profiles – For managed endpoints, you can install FortiClient with a certificate profile that automatically imports the necessary Fortinet root certificates.
Evaluating and implementing such automation should be part of your network security strategy when using Fortinet firewalls with SSL inspection.
This avoids having to manually install SSL certificates and ensures a consistent security posture across your fleet of client devices.
Conclusion
Certificate errors like “Fortinet root certificate required but not installed” are commonly faced when implementing SSL inspection with Fortinet firewalls.
This article covers a wide range of troubleshooting tips to isolate, diagnose and resolve such errors quickly. Automation techniques can also be implemented to minimize certificate issues for large networks.
Equipped with troubleshooting knowledge and preventative measures, you can tackle Fortinet certificate problems efficiently and deliver seamless secure access.
Frequently Asked Questions on Fortinet Certificate Issues
Why am I getting “Fortinet root certificate required but not installed” error?
This error occurs when your Fortinet firewall is decrypting and inspecting HTTPS traffic using SSL inspection. The firewall presents its own Fortinet certificate to your device, but the required Fortinet root certificate is missing on your device hence not trusted.
Where do I download the Fortinet root certificate?
Log into your Fortinet firewall, go to Security Profiles > SSL Inspection and download the certificate from the certificate-inspection SSL inspection profile. Alternately, you can contact Fortinet support.
How do I install the Fortinet root certificate on Windows?
Double click the certificate file, click Install Certificate, then select Local Machine and finish the wizard. Navigate to Trusted Root Certification Authorities and confirm the Fortinet root certificate is listed.
How do I install the Fortinet root certificate on Mac?
Double click the certificate file to open Keychain Access then select the certificate. Expand Trust and set to Always Trust. Enter administrative password if prompted.
How do I install the Fortinet root certificate on Linux?
Copy the Fortinet certificate file to /usr/local/share/ca-certificates directory then run ‘update-ca-certificates’ to update the trusted CA store.
How do I install the Fortinet root certificate on Firefox or Chrome browser?
Manually import the Fortinet root certificate in Firefox or Chrome browser’s certificate manager and set it as trusted.
Can I prevent certificate errors by using a custom self-signed certificate?
Yes, you can create a new self-signed certificate, upload it to the Fortinet firewall and configure it for use in the SSL inspection profile instead of the default Fortinet certificate. This avoids trust errors.