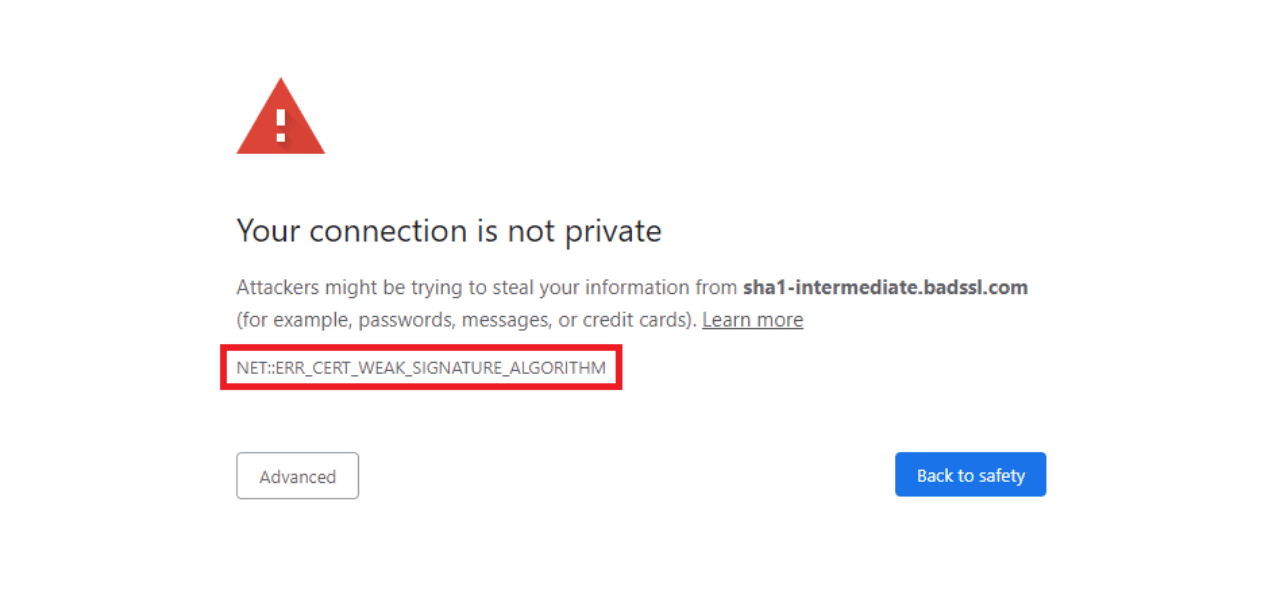
What is SSL Errros iPhone?
SSL errors on iPhones occur when there’s a problem with the secure connection between your device and a website or app. These errors appear as warnings that tell you the connection is not private or secure. Common causes include incorrect date and time settings, outdated iOS software, or problems with the website’s security certificate.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) protects your data during transmission, and these errors are safety measures to prevent potential security risks. Users can fix most SSL errors by checking their iPhone’s settings, clearing browser data, or updating their iOS version. In some cases, the website itself may have security certificate issues that need fixing.
Key Takeaways
- SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer and helps encrypt data sent over the Internet. SSL errors on iPhone occur when an SSL certificate is faulty.
- Common iPhone SSL errors include ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR iPhone, NSURLErrorDomain error -1012, and SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER. These are often caused by out-of-date software or certificates.
- To fix most SSL errors on your iPhone, update your software, apps, and certificates. You can also toggle settings like Date & Time and Airplane mode off and on.
- For specific error codes, solutions include clearing cookies and cache, resetting network settings, or contacting your ISP or the website owner.
- If the error persists, it may be an issue on the website’s end, not your iPhone. You can email the site owner to resolve it.
- To prevent SSL errors, keep your iPhone and apps updated, only install trusted profiles and certificates, and don’t jailbreak your device.
Why has an SSL error occurred on iPhone?
There are a few potential causes of SSL errors on your iPhone:
- Outdated iOS software: If you haven’t updated your iPhone to the latest iOS version, it may not support newer security protocols required by certain websites. Updating can fix associated SSL issues.
- Outdated apps: Similarly, apps that aren’t up-to-date may trigger SSL errors if they don’t support modern encryption standards. Update all apps to eliminate potential issues.
- Outdated Certificate: iPhones come preloaded with trusted root certificates from major certificate authorities that validate SSL connections. However, these can become outdated. Updating your iPhone’s certificates will resolve SSL errors caused by expired or untrusted certificates.
- Website issues: If the website’s SSL certificate is invalid, self-signed, expired, or doesn’t match the domain, your iPhone won’t trust the connection, leading to SSL errors. The website owner will need to update their SSL certificate configuration.
- Jailbroken iPhone: Jailbreaking bypasses the iPhone’s security controls, which can cause SSL errors to appear even on trusted sites. The only fix is to reverse the jailbreak.
- Incorrect date & time: If your iPhone’s date and time settings are inaccurate, SSL certificate validation checks will fail, disrupting secure connections.
- VPN or firewall blocking: A VPN or firewall that blocks certain ports or protocols may interfere with the iPhone’s ability to establish SSL-encrypted connections.
- Too many certificates: Having excessive trusted certificates installed can slow down the validation process and cause timeouts that lead to SSL errors.
In most cases, the issue is either with the website’s SSL certificate or configuration or with your iPhone blocking secure SSL connections. The good news is that there are steps you can take to troubleshoot and fix many common SSL errors.
What are the Common SSL Errors on iPhones
Some common SSL errors you may encounter on your iPhone include:
- SSL_ERROR_BAD_CERTIFICATE: The server certificate is invalid or cannot be verified. This typically indicates an issue with the website’s SSL certificate.
- SSL_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED_VERSION: The version of SSL/TLS used by the website is not supported by your iPhone. This indicates that the website needs to update to a newer SSL version.
- NSURLErrorDomain error -1202: This general SSL connection error means your iPhone cannot establish a secure connection to the server. It can occur for multiple reasons.
- ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR: Your iPhone cannot connect to the server using SSL, often due to an issue with the server’s configuration.
- NSURLErrorServerCertificateUntrusted: Your iPhone does not trust the SSL certificate, usually because it is self-signed certificate rather than issued by a certificate authority.
So, if you encounter an SSL error on a website, the exact error message can help determine if the problem is with the website’s SSL setup or an issue on your iPhone.
How to Fix SSL Error on iPhone [10 Easy Steps]
In most cases, iPhone SSL errors can be easily fixed by the user. Try these troubleshooting steps:
- Update your iPhone software
- Update all apps
- Update trusted certificates
- Toggle Airplane Mode
- Toggle Date & Time setting
- Clear cookies and cache
- Reset network settings
- Try a different browser
- Contact the website owner
- Email the certificate authority
Step #1 Update your iPhone software.
Make sure your iPhone is running the latest iOS version. Go to Settings > General > Software Update and install any available updates. The latest iOS release may resolve SSL bugs and add support for new security protocols.
Step #2 Update all apps
Out-of-date apps can trigger SSL issues in some cases. Open the App Store on your iPhone and go to Updates to install any pending app updates. This will ensure all apps support modern SSL standards.
Step #3 Update trusted certificates
iPhones come with pre-installed root certificates that sometimes need updating. To refresh your trusted certificates:
- Go to Settings > General > About and wait for any pending updates to install.
- Alternatively, install the latest iOS software update, which includes new root certificates.
Step #4 Toggle Airplane Mode
Temporarily enabling Airplane Mode disables all connections, essentially resetting your network systems. To toggle Airplane Mode:
- Open Settings and toggle Airplane Mode on.
- Wait 30 seconds, then switch it off.
- Try loading the website again.
Step #5 Toggle Date & Time setting
If the SSL error mentions an invalid certificate date, your iPhone date and time may be inaccurate. To reset:
- Go to Settings > General > Date & Time.
- Turn Set Automatically off and then back on again.
- If that doesn’t work, manually set the correct date and time.
Step #6 Clear cookies and cache
Clearing your iPhone’s cookies and cache can eliminate problematic files causing SSL errors:
- In Safari, go to Settings > Safari > Clear History and Website Data.
- Delete all cookies and data. Then, try the site again.
Step #7 Reset network settings
For persistent system-wide SSL issues, reset your network settings back to default:
- Go to Settings > General > Reset > Reset Network Settings.
- This will erase all network settings, so you’ll need to rejoin WiFi networks.
Step #8 Try a different browser.
If you’re getting an SSL error in Safari, try launching the website in a third-party browser like Chrome or Firefox, which may handle SSL differently.
Step #9 Contact the website owner.
For certificate issues like SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER, the problem is on the website’s end. Contact the site admin and have them verify and update their SSL certificate configuration.
Step #10 Email the certificate authority.
If an issuer like Verisign or Digicert is identified in the SSL error, email their support team to check if they have revoked the affected Certificate. They may be able to resolve the problem.
How to Fix Specific iPhone SSL Errors
Here are solutions for some of the most common SSL errors seen on iPhones:
ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR iPhone
This means your iPhone’s iOS version doesn’t support the protocol or cipher suites required to establish an SSL connection with the server.
To fix it, update your iPhone software. Go to Settings > General > Software Update and install the latest iOS version. This will ensure your iPhone supports modern security protocols.
Alternatively, contact the website owner and suggest they support TLS 1.2 or higher and use strong ciphers like AES 256-bit encryption.
NSURLErrorDomain error -1012 iPhone
The generic error -1012 indicates your iPhone can’t establish an SSL connection with the server to encrypt data transfer.
Potential fixes include:
- Updating your trusted root certificates on iPhone: Go to Settings > General > About and wait for the certificates to update.
- Clearing Safari history and data: This removes problematic cached files.
- Resetting network settings: Go to Settings > General > Reset and tap Reset Network Settings.
- Installing iOS and app updates: Bring software up-to-date.
- Contacting the website owner: Ask them to check their SSL certificate configuration.
SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER iPhone
This error means your iPhone doesn’t recognize or trust the issuer of the website’s SSL certificate, so the Certificate cannot be validated.
To resolve it:
- Update your iPhone’s trusted root certificates: Apple regularly adds new trusted roots. Go to Settings > General > About and wait for any pending updates to install. This will update your root store.
- Contact the website owner: Let them know you are getting an SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER error. I suggest they generate a new SSL certificate from a trusted, well-known authority like DigiCert or Comodo. Self-signed certificates will cause this.
- Install the issuer’s root certificate: If you know and trust the source of the website’s Certificate, you can install the issuing CA’s root certificate directly on your iPhone. Go to Settings > General > Profiles & Device Management and import the root certificate. However, this reduces security, so only do this if necessary.
- Try bypassing the error: Some browsers may allow you to bypass the error and continue, but this could be risky. Only bypass if you trust the site and connection.
SEC_ERROR_EXPIRED_CERTIFICATE iPhone
This error occurs when the website’s SSL certificate has already expired. Certificates are only valid for a set period, usually 1-2 years. When the expiration date passes, the Certificate is no longer trusted.
To fix this, the website owner needs to renew and update the SSL certificate on their web server. As a user, you can email the website administrator to notify them that your SSL certificate has expired.
Some temporary workarounds include:
- Accessing the site without SSL (HTTP instead of HTTPS) if that’s an option.
- Adding an exception in your browser if the site is trusted. However, this comes with some security risks.
- Trying the site in a different browser, as browser certificate caches differ.
NET::ERR_CERT_DATE_INVALID iPhone
This error indicates the effective date configured on the website’s Certificate is incorrect. The valid from and valid to dates are either in the future or past.
To resolve this, the web admin needs to regenerate their SSL certificate with proper validity dates in the certificate signing request (CSR). They can make the new Certificate effective immediately.
If the server’s clock is inaccurate, ensuring it’s set to the right date and time may also fix the invalid date error.
As a user, you’ll have to wait for the site to fix their Certificate. Try accessing the page later once they have deployed an updated certificate with the proper validity period specified.
SEC_ERROR_UNTRUSTED_ISSUER iPhone
This means the website’s SSL certificate issuer is not on your iPhone’s list of trusted certificate authorities. By default, most iPhones trust well-known CAs like Comodo, Symantec, GoDaddy, GlobalSign, Digicert, and Verisign.
To resolve untrusted issuer errors:
- Update your iPhone’s root certificates to see if the issuer is now trusted. Go to Settings > General > About.
- Contact the website owner and suggest that they obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted, well-known CA. Self-signed certificates will show this error.
- Install the issuing CA’s root certificate directly if you know and trust the source. But exercise caution as this reduces security.
How to Prevent SSL Errors on iPhone
Here are some tips to avoid those pesky SSL errors from popping up in the first place when browsing on your iPhone:
- Keep your iPhone and apps updated to the latest versions at all times. This ensures maximum compatibility with the newest encryption standards websites implement.
- Only install root certificates from trustworthy sources, such as your employer, school, or government agency. Avoid directly installing self-signed certificates.
- Don’t jailbreak your iPhone, as it bypasses security controls and opens you up to SSL vulnerabilities.
- Enable automatic date and time settings and ensure they are accurate. Certificates rely on correct dates and times.
- Clear your cookies and history periodically to remove any cached corrupt files that may disrupt SSL connections.
- Reset network settings occasionally as a general troubleshooting step for connectivity issues.
- Notify website owners whenever you encounter an SSL error on their site so they can properly configure their SSL certificates.
- As a site owner, follow best practices for deploying SSL certificates, such as using strong 2048+ bit keys, SHA-2 hashing, and industry stapling.
Final Thoughts
SSL errors on iPhones usually occur due to invalid certificates or unsupported protocols on the problematic websites. Although irritating, these errors can typically be resolved by troubleshooting your iPhone’s settings, updating iOS, clearing Safari data, and contacting the website owner if needed. Following the solutions outlined in this guide should help you diagnose and fix common SSL errors, allowing you to access websites and apps again on your iPhone securely.
Frequently Asked Questions about SSL Errors on iPhone
Why do I keep getting SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER on my iPhone?
The SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER error appears when your iPhone doesn’t recognize the authority that issued the website’s SSL certificate. This occurs when the Certificate is self-signed or issued by a small certificate authority that is outside your iPhone’s trusted store. The website needs to get a certificate from a well-known authority like Symantec or Comodo.
How do I update root certificates on my iPhone?
You can update expired or untrusted root certificates on your iPhone by going to Settings > General > About. If certificate updates are available, they will install automatically. Also, make sure you have upgraded to the latest iOS version, which contains the newest certificate bundle.
Can I fix ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR by jailbreaking?
No, jailbreaking your iPhone is not recommended if you want to resolve SSL errors. Jailbreaking bypasses the iPhone’s security controls, which often causes more SSL certificate issues than fewer. Updating your iOS system software is the best way to add support for modern protocols that sites require.
Why do I get SEC_ERROR_EXPIRED_CERTIFICATE on some websites?
You’ll see the SEC_ERROR_EXPIRED_CERTIFICATE when the website’s SSL certificate has passed its validity period and expired. The site needs to renew its Certificate and update it on the server. As a user, please email the web admin to notify them or try the site again later once the Certificate is replaced.
How can I check the expiration date of a website’s Certificate?
On iPhone, tap the lock icon next to the URL and tap Certificate. In the popup, look under Expires On to see the expiration date. If it’s in the past, it indicates an expired certificate causing SSL errors.
What causes NSURLErrorDomain -1012 on iPhone?
NSURLErrorDomain -1012 is a general SSL protocol error indicating your iPhone cannot establish an encrypted connection with the server. It may occur if your iOS or apps need to be updated, certificates are invalid, settings are incorrect, or the website has a problem with their SSL certificate.
Is it safe to ignore the SEC_ERROR_UNTRUSTED_ISSUER warning?
No, it is not safe to ignore SEC_ERROR_UNTRUSTED_ISSUER errors. This means your iPhone does not trust the certificate authority, and the connection may be intercepted by a bad actor. Avoid the site and notify the owner until they install a certificate from a well-known trusted authority.
How do I email a website owner about their SSL certificate problem?
To email the website owner, find their contact email on the site’s Contact Us or About Us page. If you cannot find it, use Whois to look up the site owner’s email. In your message, describe the SSL error you are getting and the steps to reproduce it. They can then troubleshoot the issue on their end.

Priya Mervana
 Verified Web Security Experts
Verified Web Security Experts
Priya Mervana is working at SSLInsights.com as a web security expert with over 10 years of experience writing about encryption, SSL certificates, and online privacy. She aims to make complex security topics easily understandable for everyday internet users.