Setup HTTP/2 on IIS Web Server
HTTP/2 represents a major update to the HTTP protocol which enhances web performance through its multiplexing features and header compression and server push capabilities. The main purpose of HTTP/2 is to enhance client-side performance by speeding up page loading in web browsers. The server implementation of HTTP/2 results in a minimal increase of CPU usage.
What You Need Before Getting Started
Before enabling HTTP/2 on IIS, ensure you meet these requirements:
| Component | Requirement |
| Operating System | Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016 and later |
| IIS Version | IIS 10.0 or higher |
| SSL Certificate | Valid SSL certificate (HTTP/2 requires HTTPS) |
| Domain Binding | Properly configured HTTPS binding |
Your Quick Prerequisites Checklist
- IIS 10.0 or newer is installed and running: Check this in Server Manager or Windows Features
- You have a valid SSL certificate ready: Either purchased from a CA or generated for testing
- HTTPS binding is properly set up: Your site should already be accessible via https://
- You have admin rights on the server: You’ll need full administrative access to make these changes
How to Enable HTTP/2 on IIS (Complete Steps)
Step 1: Install and Configure IIS
To start the process on Windows 10 users should click Start then navigate to Control Panel and select Programs and Features before clicking “Turn Windows Features On or Off.” The list contains requirements which you need to select Internet Information Services to activate IIS.
When using Windows Server you should follow these steps.
- Launch Server Manager from your taskbar or Start menu
- Click “Add Roles and Features“ in the main dashboard
- Select “Web Server (IIS)“ role from the server roles list
- The wizard will lead you through the rest of the installation process after you select Web Server (IIS) role.
Step 2: Install SSL Certificate
HTTP/2 requires HTTPS connections. Follow these steps:
1. Get your SSL certificate ready:
- Buy from a best SSL certificate providers like DigiCert, Sectigo, or SSL.com for production sites
- Create a self-signed certificate if you’re just testing (not recommended for live sites)
2. Install the certificate into IIS:
- Open IIS Manager from your Start menu or administrative tools
- Click on your server name in the left connections panel
- Double-click the “Server Certificates“ icon in the main features view
- Click ”Import…“ in the Actions panel and browse to your certificate file
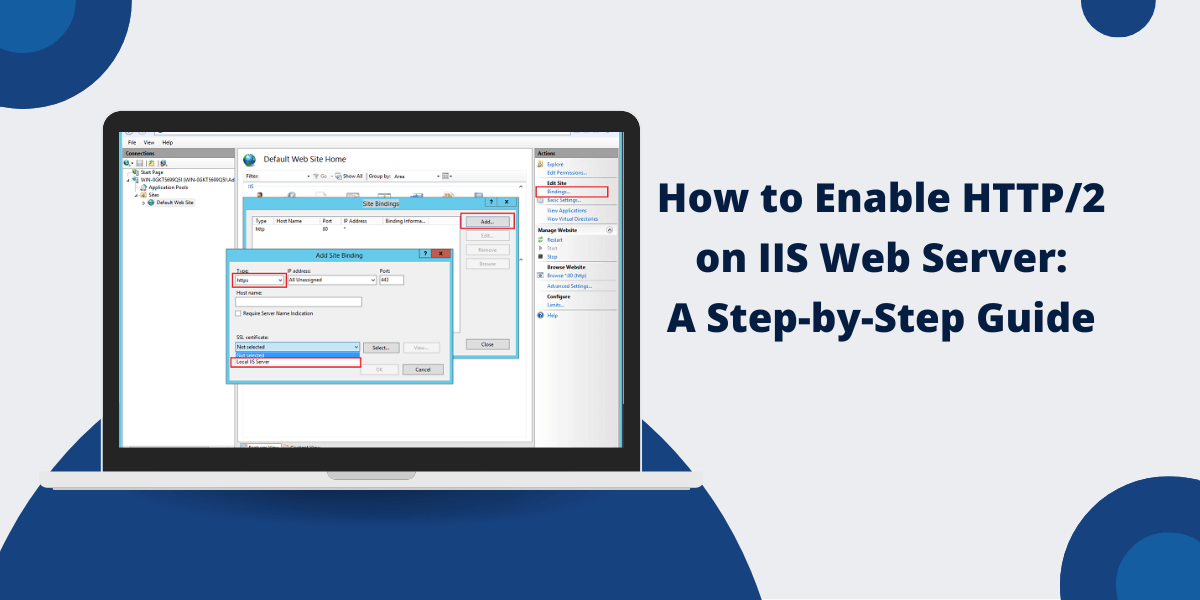
Step 3: Configure HTTPS Binding
- Launch IIS Manager from your Start menu or Server Manager
- Find your website in the left-side connections tree and click on it
- Right-click on your site name and choose ”Edit Bindings…” from the context menu
- Click the “Add…“ button to create a new HTTPS binding:
| Setting | Value |
| Type | https |
| IP Address | All Unassigned (or specific IP) |
| Port | HTTPS Port 443 |
| SSL Certificate | Choose the friendly name of the SSL certificate that you added earlier |
- Click “OK” to save your new binding: Your site should now be accessible via HTTPS
Step 4: Enable HTTP/2 (Automatic)
The HTTP/2 protocol functions automatically on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016+ systems when these requirements are satisfied:
- Your HTTPS binding is working correctly: Test by visiting https://yoursite.com
- A valid SSL certificate is installed and active: No browser security warnings
- IIS 10.0 or newer is running: Check your Windows version to confirm
How to Verify HTTP/2 is Working
Method 1: Browser Developer Tools
- Open your website in Chrome, Edge, or Firefox
- Press F12 to open the browser’s Developer Tools
- Click on the “Network“ tab at the top of the developer panel
- Refresh your webpage (F5 or Ctrl+R) to capture the requests
- Look for the “Protocol“ column and check for “h2” entries (this means HTTP/2 is working!)
Method 2: IIS Log Analysis
Enable the Protocol Version field in IIS logs to track which requests are going via HTTP/2, HTTP/1.1 etc. In the Internet Services Manager UI, this can be found under the Logging feature, through Select Fields.
Here’s how to track HTTP/2 in your logs:
- Launch IIS Manager from your Start menu or Server Manager
- Find and click on your website in the left-hand connections panel
- Look for the “Logging” icon in the main features view and double-click it
- Click the “Select Fields…” button to customize what gets logged
- Scroll down and tick the “Protocol Version” checkbox: this will show you h2 vs http/1.1
- Hit “Apply” in the Actions panel to save your changes
Pro tip: After enabling this, check your log files in C:\\inetpub\\logs\\LogFiles\\ to see the protocol column showing “HTTP/2.0” for successful connections!
Method 3: Command Line Verification
# PowerShell command to check HTTP/2 support curl -I --http2 https://yoursite.com
Advanced HTTP/2 Performance Tuning
Stream Prioritization Settings
Stream Prioritization allows the client to prioritize the delivery of certain streams, ensuring that critical resources are loaded first. You can configure Stream Prioritization in IIS using the HTTP/2 Settings frame with initial window size to 1 MB and maximum frame size to 16 KB.
Registry Tweaks (Advanced)
For fine-tuning HTTP/2 performance:
| Registry Key | Default Value | Purpose |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\System\\CurrentControlSet\\Services\\HTTP\\Parameters\\Http2MaxConcurrentClientStreams | 100 | Max concurrent streams |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\System\\CurrentControlSet\\Services\\HTTP\\Parameters\\Http2MaxFieldSectionSize | 16384 | Max header size |
Final Thoughts
The process of enabling HTTP/2 on IIS becomes simple with IIS 10.0+ and Windows Server 2016+. The HTTP/2 protocol activates automatically when HTTPS receives proper configuration with a valid SSL certificate. Your website will experience performance improvements through multiplexing and header compression and reduced latency when you focus on proper SSL setup.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is HTTP/2 in IIS?
HTTP/2 is an improved version of the HTTP protocol. IIS servers use HTTP/2 to send web content faster. The protocol reduces page load times and improves website performance through multiplexing and header compression.
Does IIS support HTTP/2?
IIS supports HTTP/2 on Windows Server 2016 and later versions. Users need Windows 10 or Server 2016 with TLS 1.2 enabled. The server requires HTTPS certificates for HTTP/2 connections.
How do I check if HTTP/2 is enabled on IIS?
Users can check HTTP/2 status through Chrome DevTools Network tab. The protocol column shows h2 for active HTTP/2 connections. IIS administrators can also verify through IIS Manager’s server settings.
What are the requirements for HTTP/2 in IIS?
HTTP/2 requires Windows Server 2016 or newer versions. The server needs valid SSL certificates. Clients must use modern browsers supporting HTTP/2. The website must run on HTTPS protocol.
Can HTTP/2 work without SSL?
HTTP/2 requires SSL certificates on IIS servers. Modern browsers only support HTTP/2 over HTTPS connections. Server administrators must install valid SSL certificates before enabling HTTP/2.
How do I test HTTP/2 connection?
Users can test HTTP/2 with online tools like KeyCDN’s HTTP/2 test. Browser developer tools show protocol versions in network requests. Chrome displays h2 for active HTTP/2 connections.

Priya Mervana
 Verified Web Security Experts
Verified Web Security Experts
Priya Mervana is working at SSLInsights.com as a web security expert with over 10 years of experience writing about encryption, SSL certificates, and online privacy. She aims to make complex security topics easily understandable for everyday internet users.