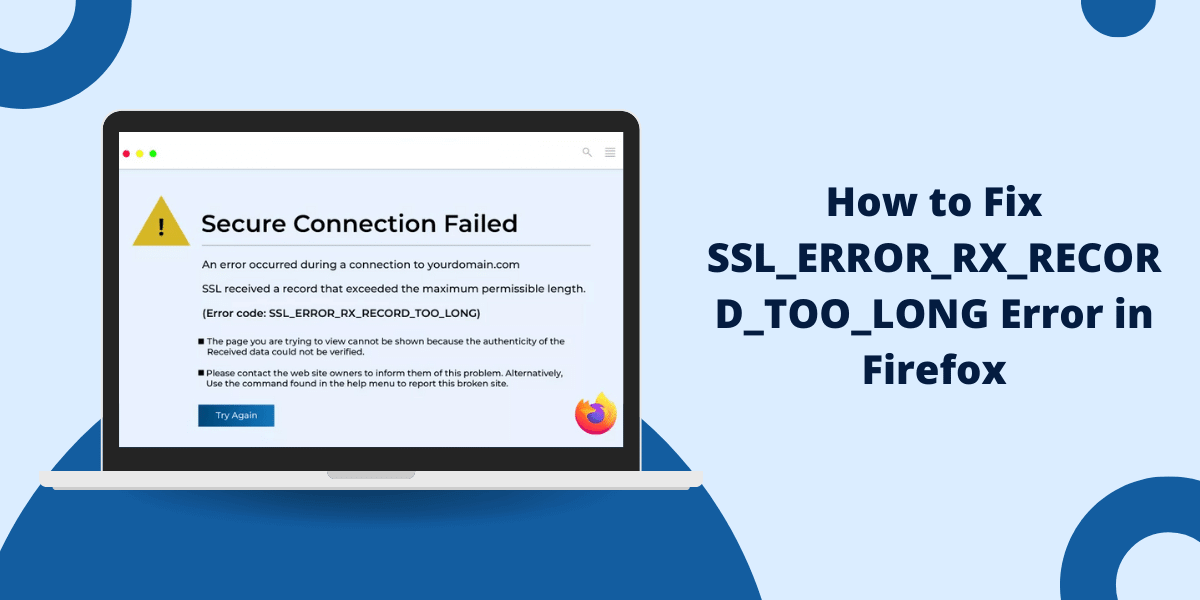
What Does SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG Error Mean?
The SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG is a common error that Firefox users may encounter when visiting certain HTTPS websites. This error indicates that the encrypted data packet received by Firefox was too large per the TLS specification.
While this error is often caused by issues on the website’s server side, there are a few things you can try on your end to resolve it.
10 Easy Steps to Fix SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER Error in Firefox
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to troubleshoot and fix the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG error in Firefox:
1. Clear Firefox Cache
Clearing your Firefox cache is one of the first things to try when encountering connection errors like SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG. A corrupt cache can cause problems with establishing secure HTTPS connections.
To clear the Firefox cache:
- Open Firefox and click on the menu button in the top-right corner.
- Select “Settings” from the menu.
- In the Settings page, scroll down to the “Privacy & Security” section.
- Under “Cookies and Site Data”, click on “Clear Data”.
- In the “Clear All History” popup, select “Cached Web Content”.
- Change the time range to “Everything” to clear the entire cache.
- Click “Clear Now”.
- Restart Firefox to complete the cache clearing.
Now try loading the website that was showing the error again in the new Firefox tab. The SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG may be resolved after clearing the corrupt cache.
2. Disable Firefox Proxy Settings
If you have configured a proxy server in Firefox, it can also be the reason behind TLS errors like SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG. The proxy may not be handling the HTTPS traffic properly.
To disable the proxy settings:
- Click the menu button and select “Settings”.
- In the Settings page, scroll down and click on “General” on the left sidebar.
- In the Network Settings section, click on “Settings”.
- In the Connection Settings popup, select “No proxy” under Configure Proxy Access to the Internet.
- Click OK to save the changes.
Now restart Firefox and try loading the website again without any proxy enabled.
3. Clear SSL State in Firefox
Firefox saves SSL certificates and other connection data for frequently accessed HTTPS websites. Corrupted SSL state can also lead to errors like SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG.
Follow these steps to clear the SSL state in Firefox:
- Type about:config in the Firefox address bar and press Enter.
- Accept the risk warning if it appears.
- In the search bar, type security.tls.version.max.
- Double click on the security.tls.version.max preference and set the value to 4.
- Search for security.ssl3.ecdhe_ecdsa_rc4_128_sha and toggle the preference to false by double clicking on it.
- Restart Firefox.
This will reset all SSL related preferences and cached data in Firefox. Now navigate to the problematic site and check if the error persists.
4. Reset Firefox to Default Settings
If none of the above steps worked, you can try resetting Firefox to factory default settings. This will clear all customizations, extensions, certificates, caches, and settings.
Here are the steps to reset Firefox:
- Click on the menu button and select “Help” > “More Troubleshooting Information”.
- In the Troubleshooting Information page, click “Refresh Firefox” on the right.
- In the refresh popup, click “Refresh Firefox” to confirm.
- When prompted again, click “Refresh Firefox” to complete the reset.
Firefox will now restore to default settings. You may need to reinstall extensions, import bookmarks, and reconfigure settings after this.
Now visit the website again and the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG should be resolved.
5. Check System Date & Time
An incorrect system date & time can also create issues with SSL certificates and cause errors like SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG in Firefox.
Follow these steps to check and update the system date & time:
- Click on the Windows Start menu and open the “Settings” app.
- Click on “Time & Language”.
- Under “Date & Time”, make sure the system date and time are correct. If not, click on “Sync now” to fetch the accurate time from online servers.
- Also check the Time Zone selected under “Additional date, time & regional settings” and change it if required.
- Restart Firefox and try visiting the website again.
6. Disable IPv6 in Network Settings
In some cases, having IPv6 enabled can cause problems with SSL connections. Disabling IPv6 may help resolve SSL errors like SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG.
Follow these steps to disable IPv6:
- Access Windows Network Settings by right clicking the network icon in the system tray and selecting “Open Network & Internet settings”.
- On the left, click “Change adapter options”.
- Right click on your network adapter and select Properties.
- Uncheck the box for “Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)”.
- Click OK to save changes.
Now restart Firefox and test if the SSL error persists on the website.
7. Update Windows Network Adapters Drivers
Outdated or buggy network adapter drivers in Windows can also interfere with SSL connections in Firefox.
Follow these steps to update your network adapter drivers:
- Open Device Manager by right-clicking on the Start menu and selecting it.
- Expand the “Network adapters” section.
- Right click on your network adapter and select “Update driver”.
- In the update driver popup, select “Search automatically for updated driver software”.
- Windows will now search and install any available driver updates.
- Restart your computer after the drivers are updated.
Now open Firefox and try loading the website again. Updating network adapter drivers could resolve the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG.
8. Disable Certain Firefox Add-ons/Extensions
Some third-party Firefox extensions that intercept web requests and traffic can cause issues with SSL connections, leading to errors like SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG.
Try disabling these common problematic extensions:
- VPN extensions
- Ad blockers like uBlock Origin and AdBlock Plus
- Privacy extensions like Ghostery and Privacy Badger
- Password managers like LastPass
- Anti-virus extensions
- Any new extension installed recently
To disable an extension:
- Click the menu button and select “Add-ons”.
- In the Add-ons Manager page, select “Extensions” on the left.
- Find the extension you want to disable and click the toggle button to turn it off.
Now visit the HTTPS website again and check if disabling the extension resolved the SSL error. You can try disabling extensions one by one to find out which one is causing the issue.
9. Remove Problematic Firefox Profile
Firefox stores your browsing data, settings, extensions etc. in a profile folder. A corrupted profile can create problems loading HTTPS sites and cause SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG.
If none of the above steps worked, try removing your Firefox profile folder and creating a new one:
Exit Firefox completely.
- Press Win + R, type %appdata% and press Enter.
- This will open your AppData folder. Navigate to Roaming > Mozilla > Firefox > Profiles.
- Delete the folder with a random name of numbers and letters.
- Open Firefox again. It will now create a new profile folder with default settings.
- Try loading the HTTPS page again in this new profile.
Creating a fresh profile should clear any corrupted Firefox data that was interfering with SSL connections.
10. Update Firefox to Latest Version
Outdated Firefox versions may not fully support the latest TLS protocols and cipher suites required for establishing HTTPS connections.
Make sure you are running the latest version of Firefox for the best SSL compatibility:
- Click the menu button and select “Help” > “About Firefox”.
- Firefox will automatically check for any updates and download them.
- Once downloaded, click “Restart to update Firefox” to complete the update process.
Updating to the latest Firefox version can resolve many SSL related errors including SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG.
Conclusion
The SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG is a common Firefox error that indicates issues establishing a TLS encrypted connection with a website.
On the browser-side, clearing Firefox cache, disabling proxy settings, resetting SSL state, resetting Firefox to default, updating network drivers, and disabling problematic extensions are some things to try.
For server-side issues, contact the website owner and suggest actions like updating TLS library, regenerating SSL certificates, disabling TLS compression and weak ciphers etc.
With a combination of browser-side and server-side troubleshooting, this TLS handshake error can be diagnosed and resolved for smooth HTTPS browsing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG error in Firefox?
This error is typically caused by a problem in the TLS handshake due to outdated ciphers or protocol versions, issues with SSL certificates, firewall interference, malware or browser extensions blocking traffic, corrupted browser cache and other factors.
Is this error specific to Firefox or can it happen on other browsers too?
This error can occur on all major browsers like Chrome, Edge etc. However, the specific troubleshooting steps would vary for each browser.
Is there a quick fix for the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG error?
There is no quick one-step fix. You will need to methodically try various browser-level and website server-level troubleshooting steps to resolve the root cause of the TLS handshake failure.
How can I determine if the error is due to my browser or the website’s server configuration?
If the error occurs consistently on one site across different browsers, it likely indicates a server issue. If it occurs inconsistently across sites on just one browser, it points to a browser problem.
Does this error mean the website has security or SSL certificate issues?
Not necessarily. The SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG is a general TLS handshake failure and does not indicate the website itself is compromised or insecure when accessing over HTTPS.