Know the Difference Between Data Protection and Data Privacy
Knowing the difference between data protection vs data privacy in current digital era is quite crucial since the Digital era is here to stay. Knowing how to protect your data in this day of internet hazards and data breaches is more crucial than ever.
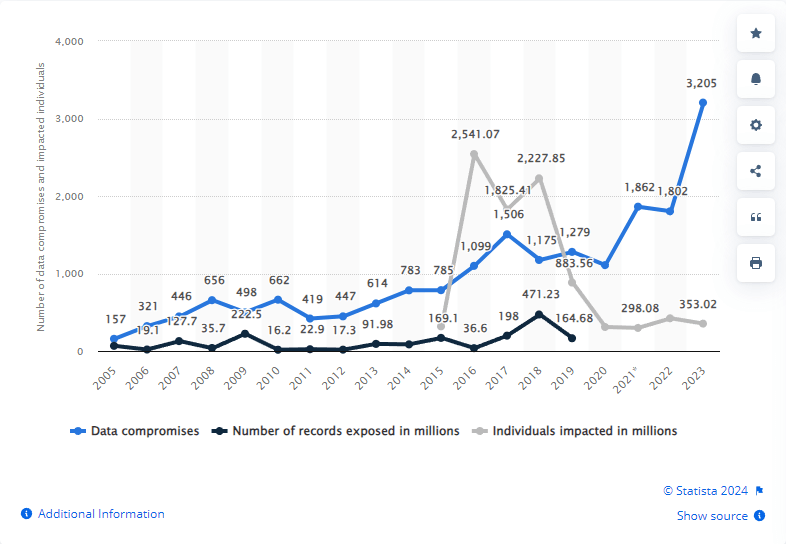
According to a Statista analysis, the US experienced over 3,200 data breaches in merely 2023. This emphasizes the need of immediate strong privacy and data security safeguards.
Data privacy and data security may so, sound similar but they are not the same thing.
While data security is about maintaining data safe from those who shouldn’t have access to it, data privacy is about ensuring that personal information is treated properly. Data protection is the super hero keeping your data safe; data privacy is the set of guidelines guiding individuals on how to handle yours.
As we look further into the issue, we will discuss more about the variances between these two concepts. We will discuss their objectives, how they intend to achieve those objectives, applicable rules, advantages and disadvantages, and challenges.
Data Protection vs Data Privacy: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Data Protection | Data Privacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures taken to safeguard data from unauthorized access and corruption. | The right of individuals to control how their personal information is collected and used. |
| Focus | Security of data. | Ethical and legal use of data. |
| Objective | Prevent data breaches and ensure data integrity. | Ensure individuals’ personal information is handled responsibly. |
| Scope | Technical measures and protocols (e.g., encryption, firewalls). | Policies and practices related to data collection, sharing, and consent. |
| Regulations | Often governed by standards like ISO/IEC 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA. | Governed by laws like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA Privacy Rule. |
| Data Lifecycle | Covers data storage, transmission, and processing. | Encompasses data collection, usage, and sharing. |
| Responsibility | IT departments, security teams, and data custodians. | Legal, compliance teams, and data protection officers. |
| Tools and Technologies | Encryption, access controls, intrusion detection systems. | Consent management systems, privacy impact assessments. |
| Risk Management | Focuses on mitigating risks of data breaches and cyber-attacks. | Manages risks related to misuse and over-collection of personal data. |
| User Impact | Users may notice security measures (e.g., multi-factor authentication). | Users have rights like access, rectification, and deletion of their data. |
| Challenges | Keeping up with evolving threats and technologies. | Balancing individual privacy rights and organizational needs. |
| Metrics | Downtime, recovery time, and data loss. | Consent rates, data subject requests, and privacy incidents. |
Understanding Data Protection And Data Privacy
It is very important to keep your info safe in today’s digital world. But what do we mean when we talk about getting data safe and private?
Let’s break it down.
A Basic Overview of Data Protection
Data protection is all about keeping data safe from people who shouldn’t be able to see it, steal it, or damage it. It makes sure that info is always available, complete, and safe. To keep your info safe, think of it as a shield for your networks.
For instance, businesses encrypt important info to keep it safe.
A study by TechRound also found that about 60% of small businesses shut down within six months of a data breach. That’s why it’s so important to keep info safe.
A Basic Overview of Data Privacy
On the other hand, data privacy means letting you decide what happens with your personal data. You can choose how your information is saved, shared, used, and collected.
Let’s say you are giving out personal information online. Wouldn’t you want to know what they’re doing with that data? Data protection makes sure that you can have complete control over your shared info online.
How then do these ideas fit together? Data privacy guards your private data in the way you choose. Data security is all about keeping data safe. Both are necessary to keep info safe.
Next, let’s dive into the objectives and focus of each.
Key Differences Between Data Protection vs Data Privacy
- Microsoft fully deploys, provisiones, and maintains HSM devices.
- It is easy to enable since Microsoft handles the HSM infrastructure.
- Microsoft personnel have administrative access to the HSM devices.
- It is well suited if you want a fully managed HSM service.
Objectives And Focus: Data Protection vs Data Privacy
Data Protection
Data security aims to keep data safe from access by persons undesired for it, loss, and theft. Its primary objectives are data privacy protection, accuracy preservation, and availability preservation. Strong security methods including encryption, safe access restrictions, and frequent security audits help to keep data safe from both within and outside hazards.
Data breaches can damage an organization’s reputation, cost money, and land in legal hotballs. To stop them, they need strong data protection measures. In addition, disaster recovery planning and data backup plans are part of data protection to make sure that businesses can keep running even if they lose data.
Data Privacy
On the other hand, data privacy means making sure that personal information is gathered, used, and shared in a way that doesn’t violate people’s rights. It stresses that users have power over their own personal data.
Have you ever thought about how much power you really have over your data? Data protection rules make sure that you can see, change, and delete your personal data as needed.
So, as we move forward, let’s explore the different strategies used to implement these objectives effectively.
Implementation Strategies: Data Protection and Data Privacy
Data Protection
The main goal of data security is to keep data safe from breaches and people who shouldn’t have access to it. Using tools like Eclypse’s secure mte, which gives companies the power to improve their data security with a full set of solutions, is a good idea.
Here are some key strategies for data protection:
- Data Lifecycle Management: Managing data from creation to deletion.
- Data Minimization: Only collect data that is necessary.
- Data Rights Automation: Automating the Enforcement of Data Rights.
- Insider Risk Management: Monitoring and mitigating risks from within the organization.
- Zero Trust: never trusting, always verifying access requests.
Data Privacy
Data privacy is about making sure that laws and rules are followed when dealing with personal data. It’s about following the user’s choices and permissions.
Some important ways to protect data privacy are:
- DSAR Management: Handling Data Subject Access Requests efficiently.
- Cookie Compliance: Ensuring that cookie usage complies with privacy laws.
- Data Inventory: Keeping an up-to-date record of all data assets.
- Intelligent Assessment: Using smart tools to assess privacy risks.
Data privacy and data security are both important for keeping users trusting you and following the rules.
So, now, we’re going to look at the regulatory scene and see how different laws affect these plans.
Regulatory Landscape: Data Privacy vs Data Protection
Regulations can be hard to understand when it comes to data safety and protection. There are different sets of rules and standards for each industry and area.
Let’s break it down.
Data Privacy
People have the right to control their own personal information, which is what data protection laws are all about.
Important rules include:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): This U.S. law protects the privacy of individuals’ health information.
- COPPA (Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act): This U.S. law ensures the privacy of children under 13 online.
- PIPEDA (Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act): Canada’s law governing data privacy.
Many of these guidelines highlight openness by advising companies to first acquire permission and inform individuals about how their data is being used. People as well as companies should be aware of the regulatory surroundings. Two advantages are preserving personal data safe from damage and maintaining compliance.
Data Protection
Data security rules seek to protect personal data from illegal access, loss, and misuse. Among the most well-known guidelines are these:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): One of the toughest European Union rules, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) thoroughly addresses all facets of data security.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): California citizens have thorough data protection rights under the U.S. state legislation known as the California Consumer Privacy Act, or CCPA.
- LGPD (Lei Geral De Proteção De Dados): Like GDPR, Brazil’s data protection law, LGPD, Lei Geral De Proteção De Dados, seeks to safeguard personal data.
These rules most of the time mandate that companies implement strict security policies, conduct frequent audits, and promptly notify any data leaks.
The next thing we’ll talk about is why data security and privacy are important.
What are the Benefits and Importance of Data Protection and Data Privacy?
Benefits & Importance of Data Protection
Keeping your data safe from anyone who shouldn’t be able to view it or access it depends on data protection. Given all the cyber risks these days, data security is really crucial. Protection of data has never been more crucial.
Data security also enables you to follow many guidelines, thereby preventing frequent fines of large amounts of money. Customers are also more likely to trust you because they know their info is safe.
Benefits & Importance of Data Privacy
Data privacy relates to our gathering, use, and distribution of private information. It’s all about allowing individuals to oversee their own data. Being honest and upfront is essential for maintaining equilibrium between data security and privacy. Openly sharing data practices, rules, and security measures with consumers helps to create confidence and demonstrates that a company takes ethical use of data highly important.
Establishing data security benefits companies and their clients alike. Data privacy governance doesn’t lock down data to keep it from being seen by anyone. Instead, it uses metadata intelligence and automatic controls to help make sure that personal and sensitive data is used correctly. We can all agree on that!
Do you understand how your information is being used and kept safe?
What are the Challenges and Best Practices
It can be hard to find your way around the world of data privacy and security. Let’s look at the problems and the best ways to solve each one.
Data Protection
Keeping up with the rules that are always changing is one of the hardest parts of protecting data. distinct locations and industries have distinct guidelines for handling, access, storing, and distributing data. You have to be alert to keep compliant. Companies can handle these issues by implementing rigorous security policies, automating security scans and checks, and providing employees extensive training.
Some of the best ways to protect info are:
- Conducting regular data protection impact assessments.
- Implementing strong encryption methods.
- Ensuring data backups are secure and regularly updated.
Data Privacy
Data privacy is all about handling data in a way that respects people’s rights. One big challenge is coming up with good privacy policies that also meet business goals. It can be hard to make rules for protecting data privacy, but it’s not impossible. Making a list of your info is an important first step.
Some of the best ways to protect data protection are:
- Regularly updating privacy policies to reflect current laws.
- Educating employees about data privacy principles.
- Using anonymization techniques to protect personal information.
After all that, let us ask you this: How do you keep your privacy rules for data up to date? How do you keep your info safe?
Final Thoughts
Maintaining our data safe and secure mostly depends on data protection and data privacy. Data privacy is all about allowing people control over their personal information, whereas data protection concentrates on shielding data from illegal access and guaranteeing its availability.
In the digital age of today, both are vital and knowing their variations can enable us to safeguard our information. Strong tactics and adopting best practices will help us to strike a balance guaranteeing the security and privacy of our data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between data protection and data privacy?
Data protection focuses on securing data through technical controls, while data privacy focuses on protecting individuals’ rights over their data.
Do data protection laws like HIPAA cover data privacy?
No, HIPAA and other data protection laws have limited coverage of privacy rights. Comprehensive data privacy laws like GDPR provide stronger privacy protections.
Is consent required for data protection compliance?
No, consent is not necessarily needed for data protection. However, it is a key principle of data privacy laws.
Can you be compliant with both data protection and data privacy?
Yes, by implementing technical safeguards and respecting individuals’ privacy rights over their data. Strong privacy protections support comprehensive data protection.
What happens if there is a data breach involving personal information?
Data privacy laws obligate notification of individuals if their data is compromised in a breach. Data protection laws don’t consistently require breach notification.
Who is responsible for data privacy and data protection compliance?
The organization that collects and processes personal data is responsible for compliance with applicable data privacy and protection laws.

Priya Mervana
 Verified Web Security Experts
Verified Web Security Experts
Priya Mervana is working at SSLInsights.com as a web security expert with over 10 years of experience writing about encryption, SSL certificates, and online privacy. She aims to make complex security topics easily understandable for everyday internet users.